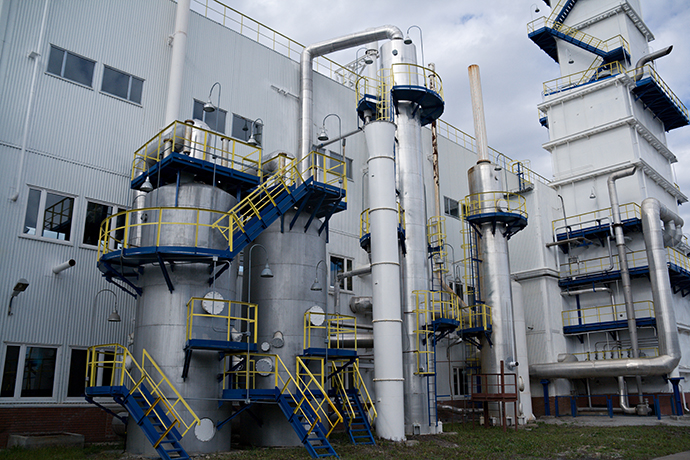
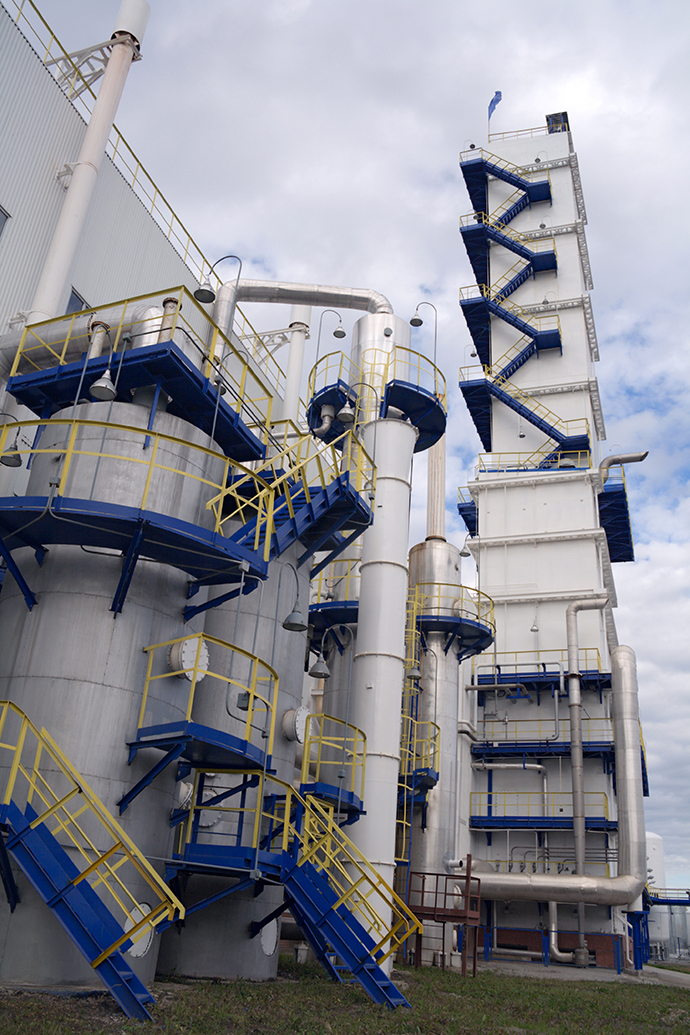
Air Separation
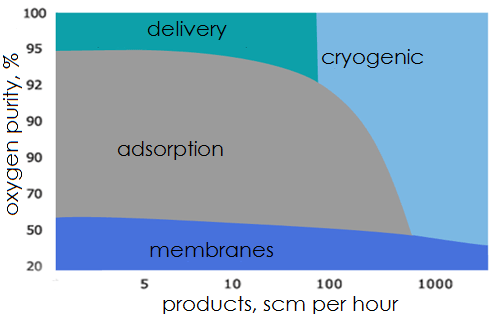
There are three types of processes used to deliver atmospheric or air separation products such as nitrogen and oxygen: cryogenic (low-temperature rectification air separation); adsorption (air separation by capturing specific contents inside the absorber vessel) and membranes (air separation by different speed of its components in passing through layers of gas separating membranes).
At the feasibility study stage of the project our technical experts scrutinize a number of factors to choose the best applicable process.
For example, in order to come up with a large amount of high quality atmospheric products (purity at least 99.2%) cryogenic units will be used. This units produce nitrogen and oxygen (as well as argon if larger units are considered) in liquid and gaseous forms.
Adsorbing and membrane units will only yield a single product – either oxygen or nitrogen and only in gaseous form. The required purity of oxygen for welding is 98.5% and it is only achievable in cryogenic separation units. Adsorption unit quality of products is lower – 95% purity at max, membrane units are even more unpresumptuous at 50% purity. It is possible, however to produce super high quality Nitrogen (99,999) both with the cryogenic and adsorption units.
Other decisive factors in choosing the suiting process are energy efficiency (power consumption per scm or ton of product), required output pressure of product, and operating requirements: number of operators per shift, servicing capabilities and periods, storage for spare parts, etc.
A simple diagram below illustrates limitations of different types of separation processes: